“Phosphine Stabilized Ruthenium Nanoparticles: the Effect of the Nature of the Ligand in Catalysis” David González-Gálvez, Pau Nolis, Karine Philippot, Bruno Chaudret and Piet W. N. M. van Leeuwen. ACS Catalysis, Volume 2, Pages 317-321, January 2012 DOI: 10.1021/cs200633k
“Phosphine Stabilized Ruthenium Nanoparticles: the Effect of the Nature of the Ligand in Catalysis” David González-Gálvez, Pau Nolis, Karine Philippot, Bruno Chaudret and Piet W. N. M. van Leeuwen. ACS Catalysis, Volume 2, Pages 317-321, January 2012 DOI: 10.1021/cs200633k
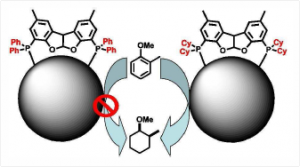
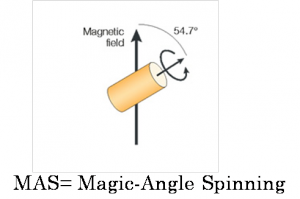
Various ligands not forming monometallic complexes were used for Ru nanoparticle stabilization, enabling the control of size, shape and electronic properties. HRMAS NMR spectroscopy allowed us to study surface-bound molecules, evidencing ligand hydrogenation and decomposition of THF during the RuNP synthesis. Catalysis studies underscore the importance of the nature of the ligands. The RuNPs were tested in the hydrogenation of aromatics, showing very high activities (TOF > 60,000 h–1, 40 bar, 393K). A pronounced ligand effect was found and dialkylaryl phosphine ligands gave the fastest catalyst.