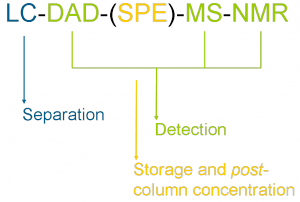
This hyphenated technique combines HPLC with three complementary detection techniques – NMR Spectroscopy, Mass Spectrometry and Diode Array Detection. It is a highly rich information source, which can be obtained by one-shot analysis.
There are three different modes of work: Flow-NMR, Stop-Flow and SPE-storage; and depending on the scientific problem one or another will be the most adequate. Continue reading HPLC-DAD-(SPE)-NMR/MS II: fundamentals and working modes