“Efficient γ-amino-proline-derived cell penetrating peptide-superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle conjugates via aniline-catalyzed oxime chemistry as bimodal imaging nanoagents”, by Cavalli S, Carbajo D, Acosta M, Lope-Piedrafita S, Candiota AP, Arús C, Royo M, Albericio F; Chem. Commun 48 (2012) p. 5322. DOI: 10.1039/C2CC17937G
“Efficient γ-amino-proline-derived cell penetrating peptide-superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle conjugates via aniline-catalyzed oxime chemistry as bimodal imaging nanoagents”, by Cavalli S, Carbajo D, Acosta M, Lope-Piedrafita S, Candiota AP, Arús C, Royo M, Albericio F; Chem. Commun 48 (2012) p. 5322. DOI: 10.1039/C2CC17937G
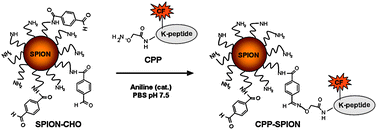
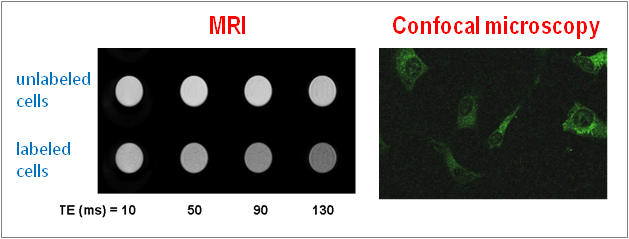
Recent advances in nanotechnology have offered new opportunities for detection, prevention, and treatment of different diseases. In this respect engineered superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) represent an advanced tool in nanomedicine because they can be loaded in a multiple and orthogonal way with drugs and probes in order to simultaneously act as molecular imaging agents and drug carriers. In this work, aniline-catalyzed oxime chemistry was employed to synthesis a novel cell penetrating peptide (CPP)-SPION nanoconjugate which exhibited a remarkably high HeLa cell internalization. Moreover, the novel CPP-SPION nanoconstruct showed fluorescent and magnetic properties in just one molecule, thus, working as bimodal probes for both confocal laser microscopy and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques.