Last September I defended my Master thesis entitled: “Medida de Acoplamientos Dipolares Residuales en Moléculas Orgánicas”
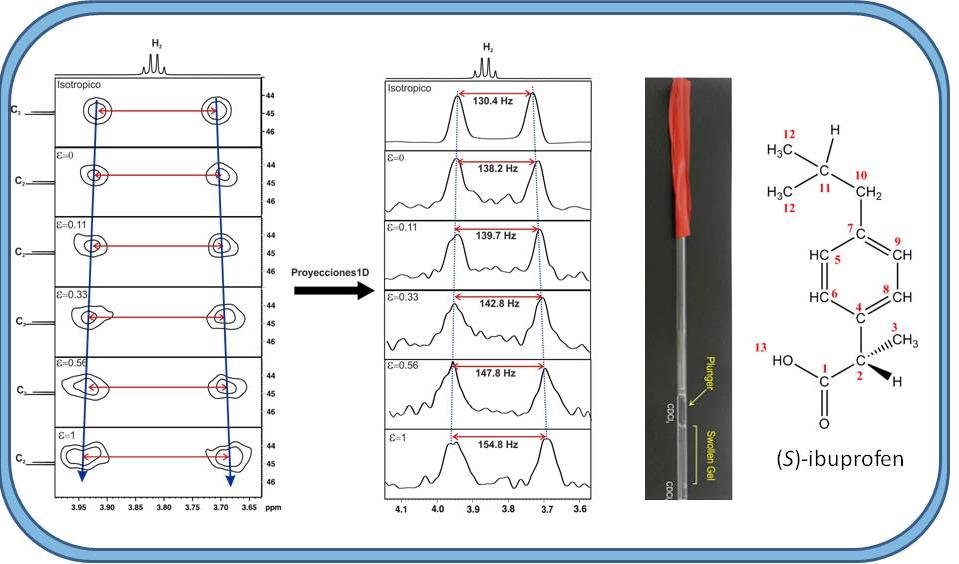 In recent years the use of Residual Dipolar Couplings (RDCs) has had a huge impact on the structure determination of biological macromolecules by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR). Its usefulness in determining the structure of small/medium-size organic compounds is increasingly more recognized. Continue reading Master thesis on NMR methods to mesure residual proton-carbon dipolar couplings in small molecules
In recent years the use of Residual Dipolar Couplings (RDCs) has had a huge impact on the structure determination of biological macromolecules by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR). Its usefulness in determining the structure of small/medium-size organic compounds is increasingly more recognized. Continue reading Master thesis on NMR methods to mesure residual proton-carbon dipolar couplings in small molecules