NaAlH4 confined in Ordered Mesoporous Carbon
NaAlH4 confined in Ordered Mesoporous Carbon
Bonatto, C.; Lindemann, I.; Nolis, P.; KieBling, A.; Baró, M. D.; Klose, M.; Giebler, L.; Rellinghaus, B.; Eckert, J.; Schultz, L.; Gutfleisch, O.
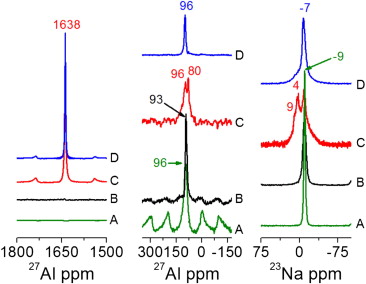
In this paper we performed a comprehensive investigation of the structural and sorption properties of a 40 wt. % NaAlH4 confined in a ordered mesoporous carbon (OMC, i.e. CMK-3) by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), 23Na{1H} and 27Al{1H} solid-state magic angle spinning-nuclear magnetic resonance (MAS-NMR).
This study evidences a remarkable improvement of the sorption kinetics of NaAlH4 due to its existence in nanometer size within the OMC. The pressure composition isotherm (PCI) analysis (for the re-absorption step) of the nanoconfined NaAlH4 would suggest an alteration of its equilibrium thermodynamic properties.