Some of the SeRMN staff presented our last research work about chirality at The first International Conference on Symmetry, Symmetry 2017, that took place from16th to 18th October in Barcelona. Find below a summary of our contribution.
Míriam Pérez-Trujillo presented a lecture entitled: “Chiral Recognition by Dissolution Dynamic Nuclear Polarization NMR Spectroscopy”
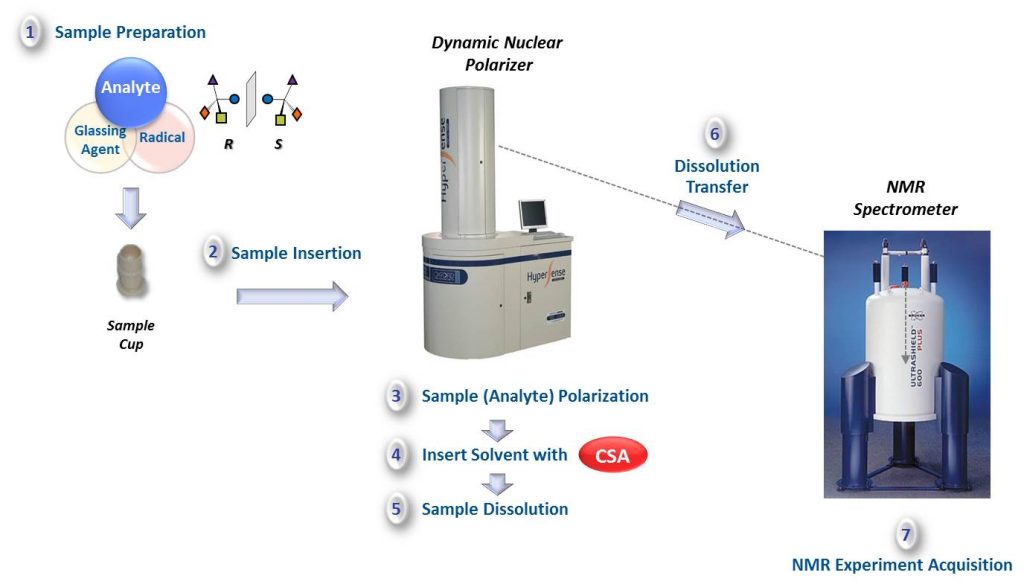
Abstract: The recognition of enantiomeric molecules by chemical analytical techniques is still a challenge. A method based on d-DNP (dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization) NMR spectroscopy to study chiral recognition was described for the first time [1]. DNP allows boosting NMR sensitivity by several orders of magnitude, overcoming one of the main limitations of NMR spectroscopy [2]. A method integrating d-DNP and 13C NMR-aided enantiodifferentiation using chiral solvating agents (CSA) was developed, in which only the chiral analyte was hyperpolarized and selectively observed by NMR. The described method enhances the sensitivity of the conventional NMR-based procedure [3] and lightens the common problem of signal overlapping between analyte and CSA. As proof on concept, racemic metabolite 13C-labeled DL-methionine was enantiodifferentiated by a single-scan 13C NMR experiment. This method entails a step forward in the chiral recognition of small molecules by NMR spectroscopy; it opens new possibilities in situations where the sensitivity is limited, for example, when low analyte concentration available or when measurement of an insensitive nucleus required. The advantages and current limitations of the method, as well as future perspectives, are discussed.