Simultaneous Enantiospecific Detection of Multiple Compounds in Mixtures using NMR Spectroscopy, by Lars T. Kuhn, Kumar Motiram-Corral, Toby J. Athersuch, Teodor Parella, Míriam Pérez-Trujillo*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020 / doi:10.1002/anie.202011727
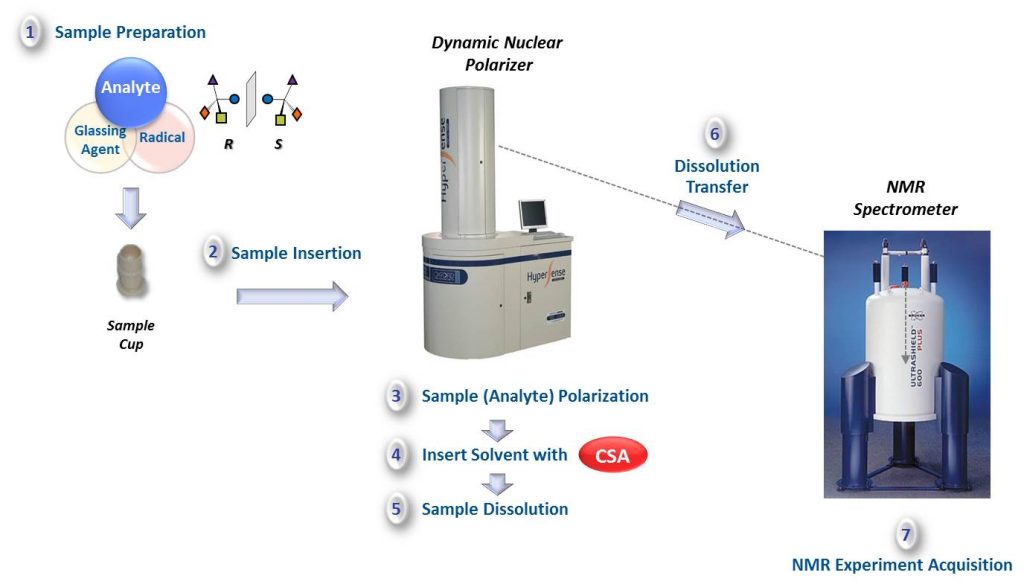
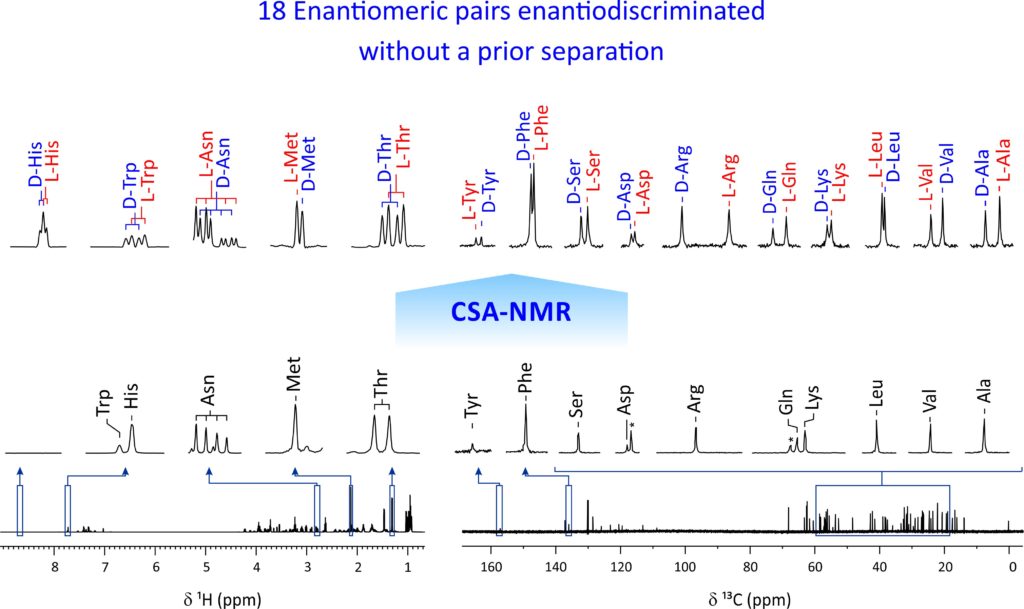
Chirality plays a fundamental role in nature, but its detection and quantification still face many limitations. To date, the enantiospecific analysis of mixtures necessarily requires prior separation of the individual components. The simultaneous enantiospecific detection of multiple chiral molecules in a mixture represents a major challenge, which would lead to a significantly better understanding of the underlying biological processes; e.g. via enantiospecifically analysing metabolites in their native environment. Here, we report on the first in situ enantiospecific detection of a thirty‐nine‐component mixture. As a proof of concept, eighteen essential amino acids at physiological concentrations were simultaneously enantiospecifically detected using NMR spectroscopy and a chiral solvating agent. This work represents a first step towards the simultaneous multicomponent enantiospecific analysis of complex mixtures, a capability that will have substantial impact on metabolism studies, metabolic phenotyping, chemical reaction monitoring, and many other fields where complex mixtures containing chiral molecules require efficient characterisation.
This work has been selected to be presented as a talk at 2021 scientific conferences:
· 42nd FGMR (German Chemical Society, Magnetic Resonance Section) Annual Discussion Meeting – Virtual, Sep 27 to Oct 1.
· SMASH- Small Molecule NMR Conference 2021 – Virtual, Aug 30 to Sep 2.
· Euromar 2021 Conference – Virtual, 5 to 8 July.
· 10th GERMN (Spanish NMR group of the Real Sociedad Española de Química) biennial & 9th IberoAmerican NMR Meeting – Virtual, 26 to 19 April.